
We export around the globe including destinations such as Kenya, Tanzania, Uruguay (South America), Uganda, Zambia, Malaysia, Mozambique , Botswana, South Sudan, Malta , Libya, Dubai, Qatar, Masqat , Kuwait, and Saudi Arabia. Our reputation precedes us and helps us garner clients from around the globe with the promise of excellent quality and unparalleled service. After establishing an impeccable repertoire with its clients in various parts of the world for our exports in high-quality Agricultural Tractors & Equipment at the most competitive prices, MADFI looks forward to extending its services further across the globe. We reiterate our pledge to our clients that we provide state of the art products at economical prices without compromising on quality or innovation. MADFI never compromises on quality.
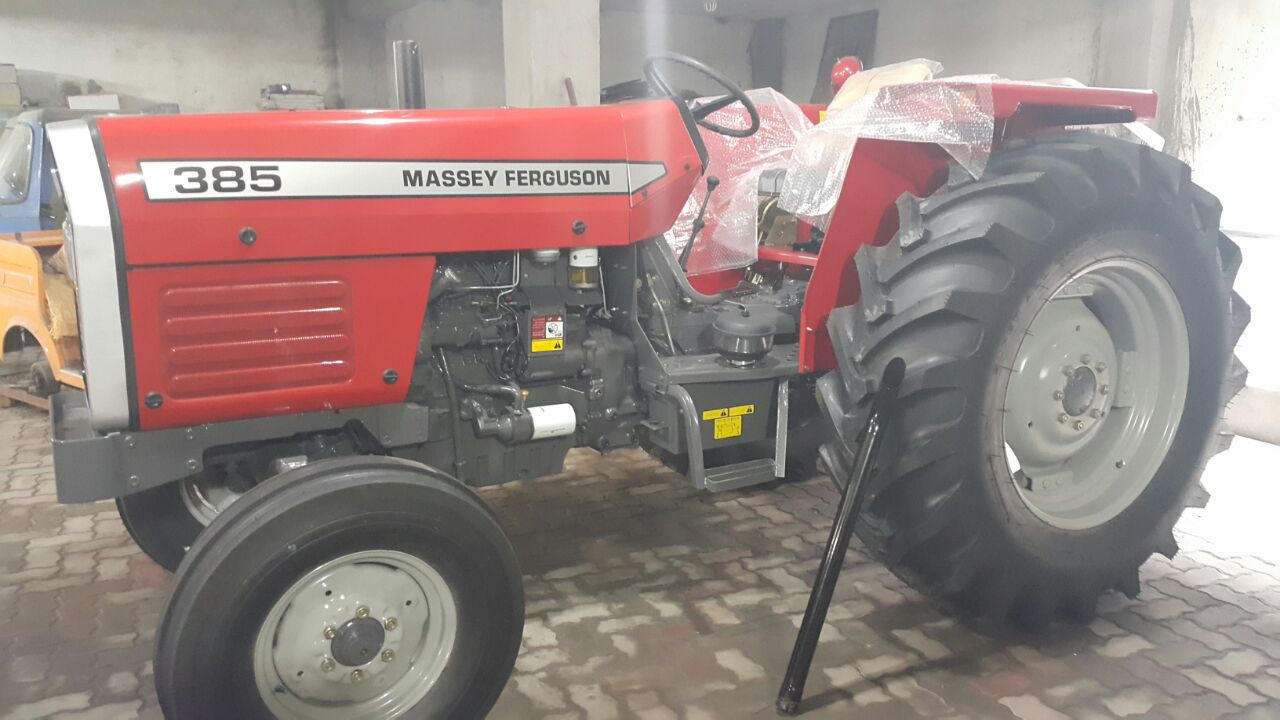
The finishing is the first stages of exporting, where the products are assembled, documented, and are inspected to satisfy customers of meeting all quality standards globally. Here all products are especially inspected to be export ready, and shipment durable.


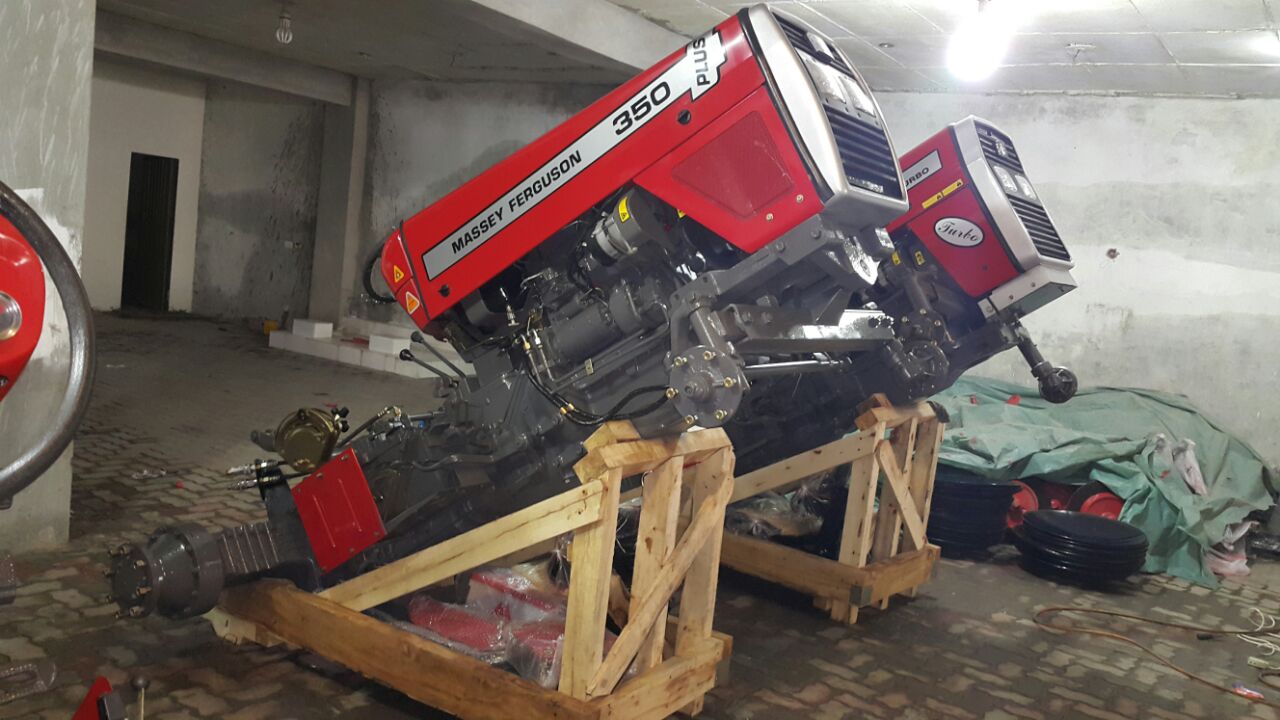
Madfi operatives personally oversee all loading and unloading procedures involved from transporting packed products from assembly outposts to ports and onto shipment containers. All the way ensuring that all Madfi products are handled with expert care and are dispatched in optimum conditions.
Special care is taken in packaging our products; we use appropriate polymer based shock absorber casing to encapsulate our machinery, inhibiting any damage that could potentially come to it by mishandling.

Algeria (Arabic: الجزائر al-Jazā'ir; Berber: Dzayer, ⴷⵣⴰⵢⴻⵔ; French: Algérie), officially the People's Democratic Republic of Algeria, is a sovereign state in North Africa on the Mediterranean coast. Its capital and most populous city is Algiers, located in the country's far north. With an area of 2,381,741 square kilometres (919,595 sq mi), Algeria is the tenth-largest country in the world, and the largest in Africa.[14] Algeria is bordered to the northeast by Tunisia, to the east by Libya, to the west by Morocco, to the southwest by the Western Saharan territory, Mauritania, and Mali, to the southeast by Niger, and to the north by the Mediterranean Sea. The country is a semi-presidential republic consisting of 48 provinces and 1,541 communes (counties). Abdelaziz Bouteflika has been President since 1999.
Cameroon (/ˌkæməˈruːn/; French: Cameroun), officially the Republic of Cameroon (French: République du Cameroun), is a country in West Africa. It is bordered by Nigeria to the west; Chad to the northeast; the Central African Republic to the east; and Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, and the Republic of the Congo to the south. Cameroon's coastline lies on the Bight of Bonny, part of the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean.

Chad (Listeni/tʃæd/; Arabic: تشاد Tshād; French: Tchad), officially the Republic of Chad (Arabic: جمهورية تشاد Jumhūrīyat Tshād; French: République du Tchad), is a landlocked country in northern Central Africa. It is bordered by Libya to the north, Sudan to the east, the Central African Republic to the south, Cameroon and Nigeria to the southwest and Niger to the west. It is the fifth largest country in Africa in terms of area.
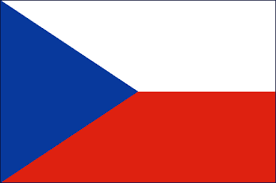
The national flag of the Czech Republic (Czech: státní vlajka České republiky) is the same as the flag of the former Czechoslovakia. Upon the dissolution of Czechoslovakia, the Czech Republic kept the Czechoslovak flag while the Slovak Republic adopted its own flag. The first flag of Czechoslovakia was based on the flag of Bohemia, and was white over red. This was identical to the flag of Poland, so a blue triangle was added at the hoist in 1920. The flag was banned by the Nazis in 1939, and a horizontal tricolor of white, red, and blue was enforced. The 1920 flag was restored in 1945.

The flag of the United Arab Emirates (Arabic: علم الإمارات العربية المتحدة) was adopted on December 2, 1971. It contains the Pan-Arab colors red, green, white, and black, which symbolize Arabian unity. Merchant ships may fly the alternative civil ensign, a red flag with the national flag in the canton.
Ghana (Listeni/ˈɡɑːnə/), officially the Republic of Ghana, is a sovereign unitary presidential constitutional democracy, located along the Gulf of Guinea and Atlantic Ocean, in the subregion of West Africa. Spanning a land mass of 238,535 km2, Ghana is bordered by the Ivory Coast in the west, Burkina Faso in the north, Togo in the east and the Gulf of Guinea and Atlantic Ocean in the south. The word Ghana means "Warrior King" in the Soninke language


The Kenyan flag is based on that of Kenya African National Union and was adopted in December 12, 1963 as the country's flag. The color black represents the people of the Republic of Kenya, red for the blood shed during the fight for independence, and green for the country's landscape and natural wealth. The white fimbriation was added later to symbolize peace and honesty. The black, red, and white traditional Maasai shield and two spears symbolize the defense of all the things mentioned above
The flag of Kuwait (Arabic: علم الكويت) was adopted on September 7, 1961, and officially hoisted November 24, 1961. Before 1961, the flag of Kuwait was red and white, like those of other Persian Gulf states at the time, with the field being red and words or charges being written in white. Until 1899, the flag consisted solely of a red field. From 1899 to 1915, the red field bore a white crescent and star and, also in white, the word "كويت" (Kuwait) styled so as to de-emphasize the word-initial K:[why?] From 1899 to 1909, the crescent-and-star symbol and the country's name were of equal height; between 1909 and 1915, the crescent


The flag of Libya was originally introduced in 1951, following the creation of the Kingdom of Libya. It was designed by Omar Faiek Shennib and approved by King Idris Al Senussi who comprised the UN delegation representing the regions of Cyrenaica, Fezzan and Tripolitania at UN unification discussions.
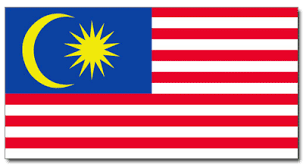
The flag of Malaysia, also known as the Jalur Gemilang (Malay for "Stripes of Glory"),[1] is composed of a field of 14 alternating red and white stripes along the fly and a blue canton bearing a crescent and a 14-point star known as the Bintang Persekutuan (Federal Star). The 14 stripes, of equal width, represent the equal status in the federation of the 13 member states and the federal government, while the 14 points of the star represent the unity between these entities.[2] The crescent represents Islam, the country's official religion; the blue canton symbolises the unity of the Malaysian people; the yellow of the star and crescent is the royal colour of the Malay rulers.[3]
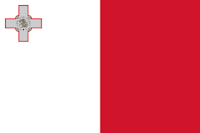
The flag of Malta (Maltese: Bandiera ta' Malta) is a basic bi-colour, with white in the hoist and red in the fly. A representation of the George Cross, awarded to Malta by George VI of the United Kingdom in 1942, is carried, edged with red, in the canton of the white stripe.
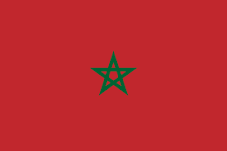
Morocco (Listeni/məˈrɒkoʊ/; Arabic: المغرب al-Maghrib; French: Maroc),[Notes 1] officially the Kingdom of Morocco,[1] is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa.[11] Geographically, Morocco is characterized by a rugged mountainous interior and large portions of desert. It is one of only three countries (with Spain and France) to have both Atlantic and Mediterranean coastlines. The Arabic name al-Mamlakah al-Maghribiyah (Arabic: المملكة المغربية, meaning "The Western Kingdom") and Al-Maghrib (Arabic: المغرب, meaning "The West") are commonly used as alternate names.

The flag of Mozambique was adopted on May 1, 1983. It includes the image of an AK-47 with a bayonet attached to the barrel, and is one of only two national flags of UN member states to feature a firearm. The other is Guatemala. Green stands for the riches of the land, the white fimbriations signify peace, black represents the African continent, yellow symbolizes the country's minerals, and red represents the struggle for independence.
The national flag of Oman (Arabic: علم عُمان) consists of three stripes (white, green and red) with a red bar on the left that contains the national emblem of Oman (Dagger and two swords). Until 1975, Oman used the plain red banner of the indigenous people. In 1970, the Sultan introduced a complete new set of national flags. Bands of green and white were added to the fly, and the national emblem, the badge of the Albusaidi Dynasty, was placed in the canton.

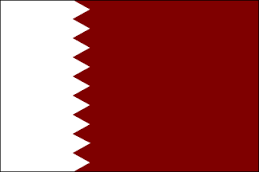
The flag of Qatar (Arabic: علم قطر) is in the ratio of 11:28. It is maroon with a broad white serrated band (nine white points) on the hoist side. It was adopted shortly before the country's declaration of independence from Britain on September 3, 1971. The flag is very similar to the flag of the neighbouring country Bahrain, which has fewer points, a 3:5 proportion, and a red colour instead of maroon. Qatar's flag is the only national flag having a width more than twice its height
The flag of Saudi Arabia (Arabic: علم المملكة العربية السعودية) is the flag used by the government of Saudi Arabia since March 15, 1973. It is a green flag featuring in white an Arabic inscription and a sword. The inscription is the Islamic creed, or shahada.

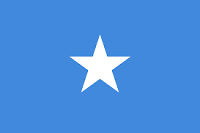
The Flag of Somalia (Somali: Calanka Soomaaliya, Arabic: علم الصومال), also known as the Somali Flag, is the official flag of the Federal Republic of Somalia. Adopted on October 12, 1954, it was designed by Mohammed Awale Liban.[1][2] Upon unification of Italian Somaliland and British Somaliland, the flag was used for the nascent Somali Republic. It was originally conceived and serves as an ethnic flag for the Somali people.[3]
The flag of Sudan (Arabic: علم السودان) was adopted on May 20, 1970, and consists of a horizontal red-white-black tricolor, with a green triangle at the hoist. The flag is based on the Arab Liberation Flag shared by Egypt, Iraq, Syria, and Yemen, that uses a subset of the Pan-Arab colors in which green is less significant. Prior to the 1969 military coup of Gaafar Nimeiry, a blue-yellow-green tricolor design was used.


The flag of Tanzania consists of a yellow-edged black diagonal band divided diagonally from the lower hoist-side corner, with a green upper triangle and blue lower triangle. Adopted in 1964 to replace the individual flags of Tanganyika and Zanzibar, it has been the flag of the United Republic of Tanzania since the two states merged that year. The design of the present flag incorporates the elements from the two former flags.
Togo (Listeni/ˈtoʊɡoʊ/), officially the Togolese Republic (French: République togolaise), is a country in West Africa bordered by Ghana to the west, Benin to the east and Burkina Faso to the north. It extends south to the Gulf of Guinea, where its capital Lomé is located. Togo covers 57,000 square kilometres (22,008 square miles), making it one of the smallest countries in Africa, with a population of approximately 7.5 million.[7]

The red and white flag of Tunisia, adopted as national flag in 1959, has its origins the naval ensign of the Kingdom of Tunis adopted in 1831 by Al-Husayn II ibn Mahmud. The star and crescent recalls the Ottoman flag and is therefore an indication of Tunisia's history as a part of the Ottoman Empire. The current official design dates to 1999.
The flag of Turkey (Turkish: Türk bayrağı, meaning "Turkish flag") is a red flag featuring a white star and crescent. The flag is often called al bayrak (the red flag) and referred to as al sancak (the red banner) in the Turkish national anthem. The current design of the Turkish flag is directly derived from the late Ottoman flag, which had been adopted in the late 18th century and acquired its final form in 1844.


The flag of Uganda was adopted on 9 October 1962, the date that Uganda became independent from the United Kingdom. It consists of six equal horizontal bands of black (top), yellow, red, black, yellow, and red (bottom); a white disc is superimposed at the centre and depicts the national symbol, a grey crowned crane, facing the hoist side
The national flag of Uruguay (Pabellón Nacional) has a field of nine equal horizontal stripes alternating white and blue. The canton is white, charged with the Sun of May, from which 16 rays extend, alternating between triangular and wavy.[1] The flag was first adopted by law on December 16, 1828, and had 19 stripes until July 11, 1830, when a new law reduced the number of stripes to nine.[2] The flag was designed by Joaquín Suárez


Yemen (Listeni/ˈjɛmən/; Arabic: اليَمَن al-Yaman), officially known as the Republic of Yemen (الجمهورية اليمنية al-Jumhūrīyah al-Yamanīyah), is an Arab country in Western Asia, occupying South Arabia, the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula. Yemen is the second-largest country in the peninsula, occupying 527,970 km2 (203,850 sq mi). The coastline stretches for about 2,000 km (1,200 mi).[6] It is bordered by Saudi Arabia to the north, the Red Sea to the west, the Gulf of Aden and Arabian Sea to the south, and Oman to the east and northeast. Although Yemen's constitutionally stated capital is the city of Sana'a, the city has been under rebel control since February 2015. Because of this, Yemen's capital has been temporarily relocated to the port city of Aden, on the southern coast. Yemen's territory includes more than 200 islands; the largest of these is Socotra.
The Flag of Yemen (Arabic: علم اليمن) was adopted on May 22, 1990, the day that North Yemen and South Yemen were unified. The flag is essentially the Arab Liberation Flag of 1952, introduced after the Egyptian Revolution of 1952 in which Arab nationalism was a dominant theme. The Arab Liberation Flag served as the inspiration for the flags of both North and South Yemen prior to unification, and the current flags of Egypt, Iraq, Sudan, and Syria.


The national flag of Zimbabwe consists of seven even horizontal stripes of green, gold, red and black with a white triangle containing a red 5-pointed star with a Zimbabwe Bird. The present design was adopted on 18 April 1980, when Zimbabwe won its independence from the United Kingdom. The soapstone bird featured on the flag represents a statuette of a bird found at the ruins of Great Zimbabwe. The bird symbolises the history of Zimbabwe; the red star beneath it officially stands for the nation's aspirations but is commonly thought to symbolise socialism.